Types of hip replacement surgery
What are the types of hip replacement surgeries? Hip replacement surgeries are classified according to how far the joint parts are going to be replaced. Orthopedic surgeons classify hip arthroplasty furthermore according to the technique of the procedure. Partial and total hip arthroplasty which are the most common types of hip replacement surgery will be discussed separately.
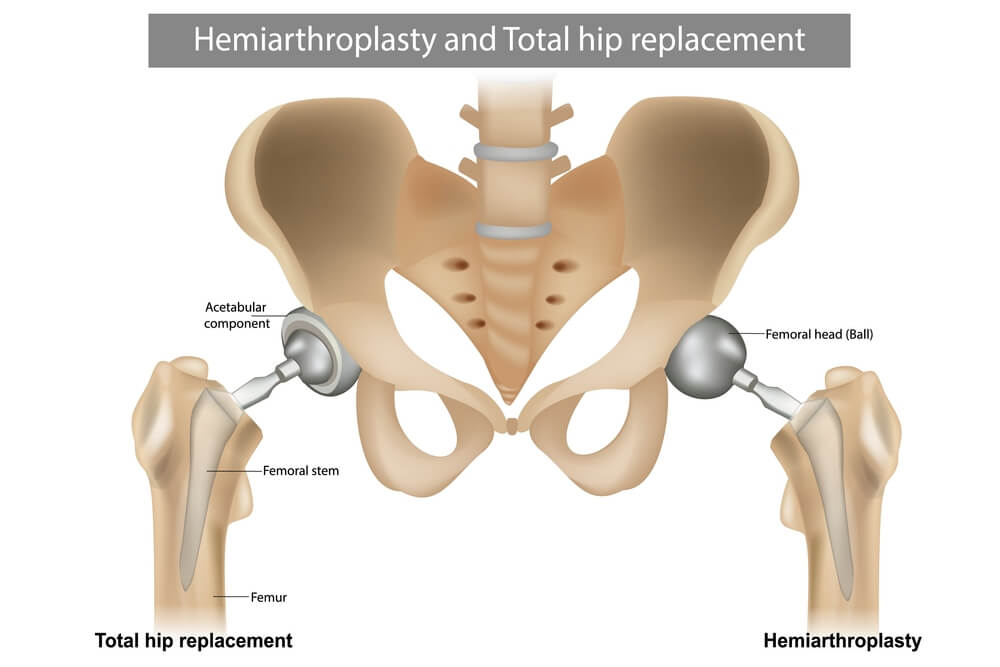
1- Total hip replacement (THR) is a surgical procedure in which both the femur head and the socket of pelvic bone are replaced with a prosthesis. THR is major surgery with a high success rate as it restores joint smooth articulation and mobility. An anesthesiologist prepares patients going to have THR by giving them general or regional anesthesia to block sensations from the lower half of their body.
Orthopedic surgeons start by making an 8 – 15 cm incision in the posterior-lateral side of the side. Anterior thigh incision isn’t preferred because it gives the surgeon limited access to the hip joint making the surgery a bit challenging. The surgeon separates the fascia and muscles covering the hip joint then dislocates the femur (thigh bone) from the pelvic bone and excises the femur head with a power saw. Then the acetabulum (the pelvic socket) is removed by a special drill forming a hemispherical cavity in which the artificial pelvic part will be placed.
Finally, the surgeon inserts a femoral stem in the thigh bone which acts as a pillar for which the femoral head will get attached. The acetabular part of the prosthesis is also placed in the pelvic bone to act as a socket for the femoral head. The two components of the prosthesis should perfectly fit each other to provide the full range of motion. The surgery usually takes about 60 – 90 minutes.
2- Partial hip replacement is a surgical procedure in which the femoral head is replaced with an artificial implant with sparing of the pelvic bone, so it is called hemiarthroplasty. Fracture of the thigh bone due to trauma or osteoporosis is the main cause of hemiarthroplasty. Partial hip replacement is less commonly performed than THA. it is believed that prosthetic implants of THA are less stable and more liable for dislocation than those of hemiarthroplasty.
Patients who are going to have hemiarthroplasty should undergo the same pre-operative examination of THA, moreover, the size of the femoral implant should be selected to fit the socket of the pelvic bone. partial hip arthroplasty goes in the same manner as done in total hip arthroplasty except remodeling the pelvic component. Surgeons test the smoothness of motion of the prosthesis with the pelvic bone by the passive articulation of the joint during the operation.
