4) Imaging
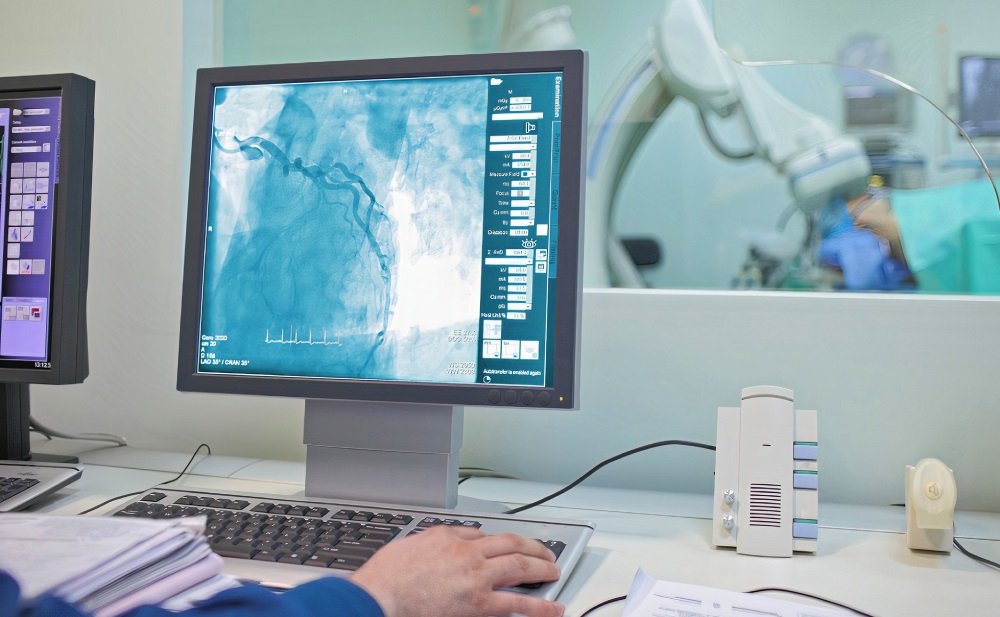
Many imaging techniques can help in the diagnosis of peripheral vascular disease through the visualization of blood vessels and blood flow through it. These techniques include:
A) Doppler ultrasonography: It is a non-invasive technique that provides an excellent way to assess the blood flow through the vessels. In this technique, the computer uses high-frequency ultrasound waves to take a picture of blood vessels.
B) Angiography (x-ray of blood vessels): In this technique, the radiologist injects a contrast dye into a leg artery to highlight the blood vessels on the x-ray, which helps to detect blockage or narrowing. This technique has disadvantages, such as being invasive, using dye makes it contraindicated in renal failure, and taking much time to do it makes it hard in acute cases when there is a need for immediate treatment.
C) Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA): Magnetic resonance imaging technique uses the power of the magnetic field to provide highly detailed for the internal structures like blood vessels. Magnetic resonance angiography saves the patients from adverse effects of exposure to irradiation besides its high accuracy. Disadvantages include the high cost, which limits its availability.
D) Computed tomography angiography (CTA): This technique depends on the x-ray to image specific areas of the body. We can do it, either by contrast dye or not. Contrast dyes provide better imaging, but we can’t use it in renal failure. Despite the disadvantage of exposure to irradiation, computed tomography has advantages that make it so useful in the emergency, such as no availability and time obstacles as MRA and its high accuracy.
Risk factors are an essential element in the management plan of peripheral vascular disease; thus, your doctor may require investigations to evaluate them, such as:
- Blood glucose for diabetes if he suspects it. If the patient has diabetes, the doctor will order “Hb-A1c” to evaluate the management plan of diabetes.
- Body mass index (BMI) for overweight or obesity
- Lipid profile for dyslipidemia: low-density lipoprotein (LDL), high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and triglycerides (TGs)
- Echocardiography and electrocardiography (ECG) to assess the cardiac functions
